The cells found in this layer are cuboidal to columnar mitotically active stem cells that are constantly producing keratinocytes. Skin Barrier. It protects the body from external factors such as bacteria, chemicals, and temperature. Sci Rep. The blood vessels in the dermis provide nourishment and waste removal from its own cells as well as from the stratum basale of the epidermis. There are many internal and external causes to skin ageing. Squamous cell carcinoma is cancer that arises from mutated keratinocytes, usually due to UV damage in individuals with Type I or II skin types light skin, blue or green eyes, red or blonde hair, burn and never tan and often appear as scaly, flaky, thick red patches that may bleed or even appear wart-like. The hypodermis is deep to the dermis and is also called subcutaneous fascia. The Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry. Bullous Pemphigoid is another blistering disease that results in tense subepidermal blisters in older populations, that are due to antibodies that target the hemidesmosomes that connect the epidermis at the level of the basement membrane to the extracellular matrix of the dermis.

The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying muscles , bones , ligaments and internal organs. Archived from the original on 11 January Editorial team. The record Dataset is supported by extensive references for cell size, cell count, and aggregate cell mass. Between the alveolar gland and the duct is the intercalary system which can be summed up as a transitional region connecting the duct to the grand alveolar beneath the epidermal skin layer.
Review Date 11/2/2023
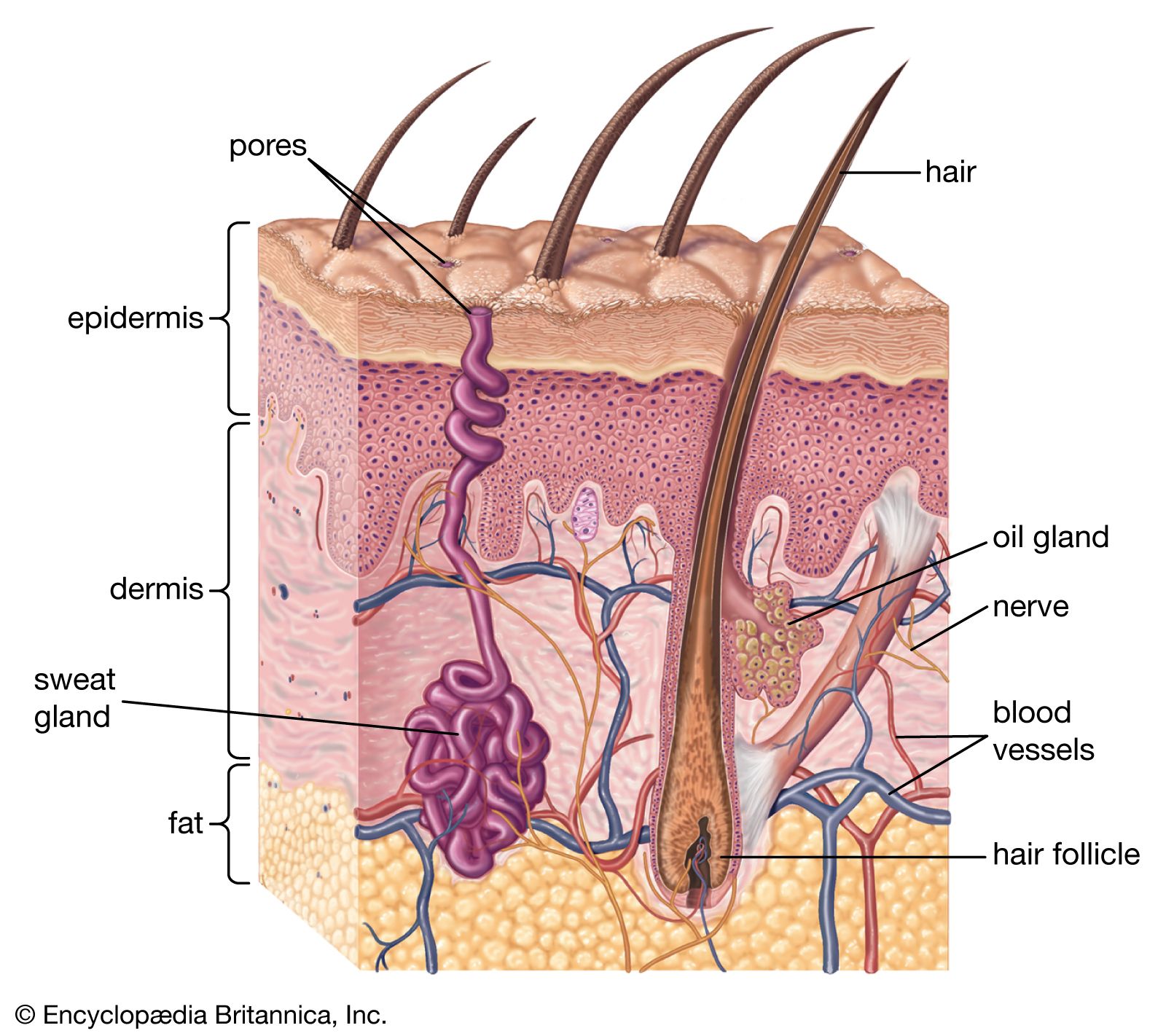
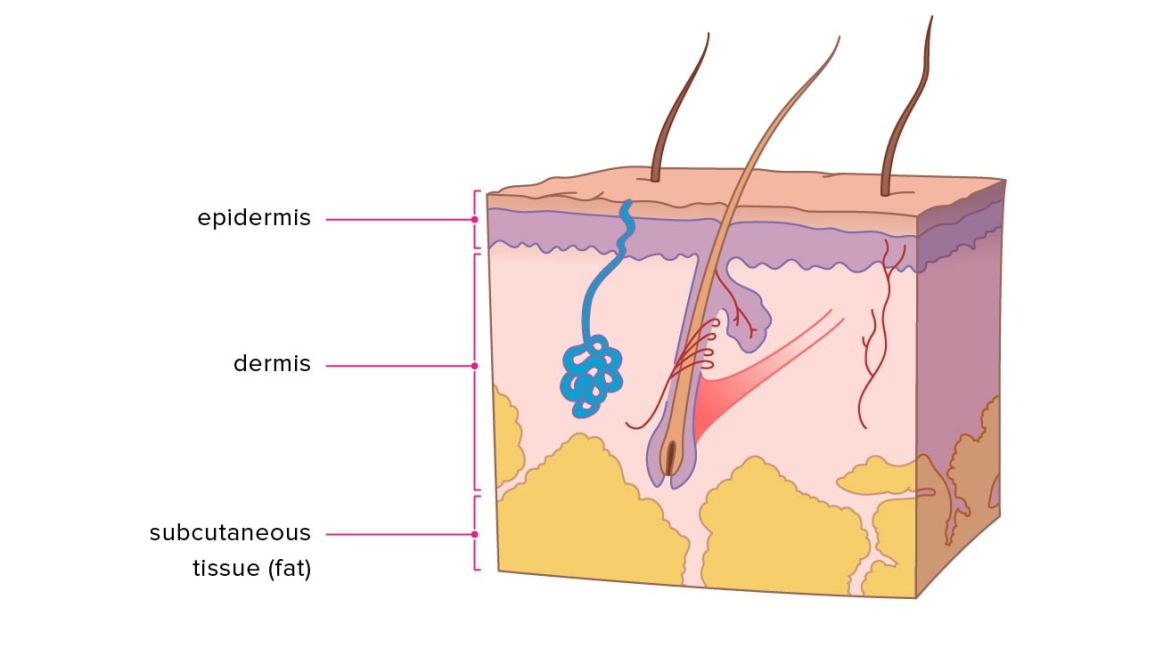
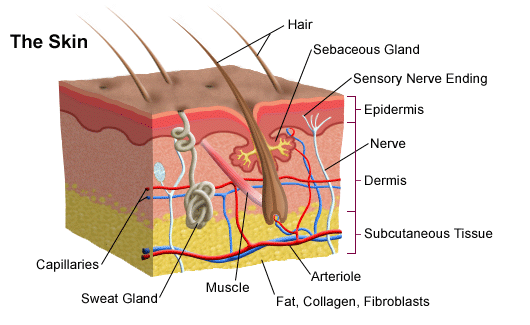
Main article: Subcutaneous tissue. The dermis contains the following: Blood vessels Lymph vessels Hair follicles Sweat glands Collagen bundles Fibroblasts Nerves Sebaceous glands The dermis is held together by a protein called collagen. They are found between cells of stratum basale and produce melanin. Retrieved 27 February Skin's outermost layer, the stratum corneum, is an effective barrier to most inorganic nanosized particles. Nerves Nerves of the skin include both somatic and autonomic nerves. Severely damaged skin will try to heal by forming scar tissue. Histology, Dermis. Skin is the first site of immunological defense by the action of the Langerhans cells in the epidermis which are dendritic epidermal T lymphocytes and part of the adaptive immune system. The skin preserves the bodies homeostasis by regulating temperature and water loss, while also serving both endocrine and exocrine functions. Aside from the dermatomes, the cells of the epidermis are susceptible to neoplastic changes resulting in various cancer types. Skin pigmentation in humans evolved to primarily regulate the amount of ultraviolet radiation UVR penetrating the skin, controlling its biochemical effects. Article Talk. Comment on this article. Skin Inc.
Skin explained - Better Health Channel
- Photoageing has two main concerns: an increased risk for skin cancer and the appearance of damaged skin, Skin.
- BMP signals from Skin epidermis inhibit the formation of placodes in nearby ectoderm.
- Skin areas with least similarity between people in species were the spaces between fingersthe spaces between toesaxillaeand umbilical cord stump, Skin.
- Article Talk.
- Mucous and granular glands are both divided into three different sections which Skin connect to structure the gland as a whole, Skin.
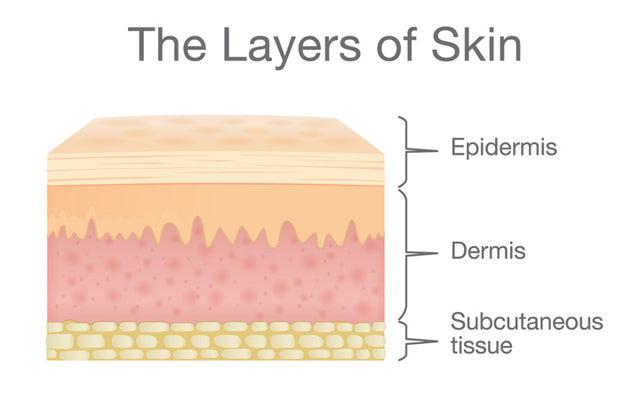
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Skin is the largest organ in the body and covers the body's entire external surface. It is made up of three layers, the epidermis, dermis, and the hypodermis, all three of which vary significantly in their anatomy and function. It also regulates temperature and the amount of water released into the environment. The thickness of each layer of the skin varies depending on body region and categorized based on the thickness of the epidermal and dermal layers. Hairless skin found in the palms of the hands and soles of the feet is thickest because the epidermis contains an extra layer, the stratum lucidum. The layers of the epidermis include the stratum basale the deepest portion of the epidermis , stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, and stratum corneum the most superficial portion of the epidermis. Stratum basale, also known as stratum germinativum, is the deepest layer, separated from the dermis by the basement membrane basal lamina and attached to the basement membrane by hemidesmosomes. The cells found in this layer are cuboidal to columnar mitotically active stem cells that are constantly producing keratinocytes. This layer also contains melanocytes. Dendritic cells can be found in this layer. Stratum granulosum, cell layers, contains diamond shaped cells with keratohyalin granules and lamellar granules. Keratohyalin granules contain keratin precursors that eventually aggregate, crosslink, and form bundles.
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering Skin body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, Skin, regulation, and sensation. Other Skin coveringssuch as the arthropod exoskeletonhave different developmental originstructure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" from Latin cutis Skin. In mammalsthe skin is an organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying musclesbonesligaments Skin, and internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibiansSkin, reptilesSkin, and birds. All mammals have some hair on their skin, even marine mammals like whalesdolphinsand porpoises that appear to be hairless. The skin interfaces with the environment and is the first line of defense from external factors. For example, the skin plays a key role in protecting the body against pathogens [3] and excessive water loss.

Skin. Anatomy of the Skin
The skin is Skin largest organ of the human body. It is soft, Skin, to allow movement, but still tough enough to resist breaking or tearing. It varies in texture and thickness from one part of the body to the next, Skin. For instance, the skin on our lips and eyelids is very thin and delicate, while skin Skin the soles of our feet is thicker and harder. Our skin is a pampers rodzaje i rozmiary indicator of our general health. If someone is sick, Skin, it often shows in their skin, Skin. The skin you can see is called the epidermis. This protects the more delicate inner layers. The bottom sheet is where new epidermal cells are made, Skin. As old, dead skin cells are sloughed off the surface, new ones are pushed up to replace them. The epidermis also contains melanin, the pigment that gives skin its colour. Skin the epidermis is the Skin.
StatPearls [Internet].
Click Image to Enlarge. The skin is the body's largest organ. It covers the entire body. It serves as a protective shield against heat, light, injury, and infection. The skin also:.
Retrieved 27 February Papillary Dermal papillae Reticular.

0 thoughts on “Skin”